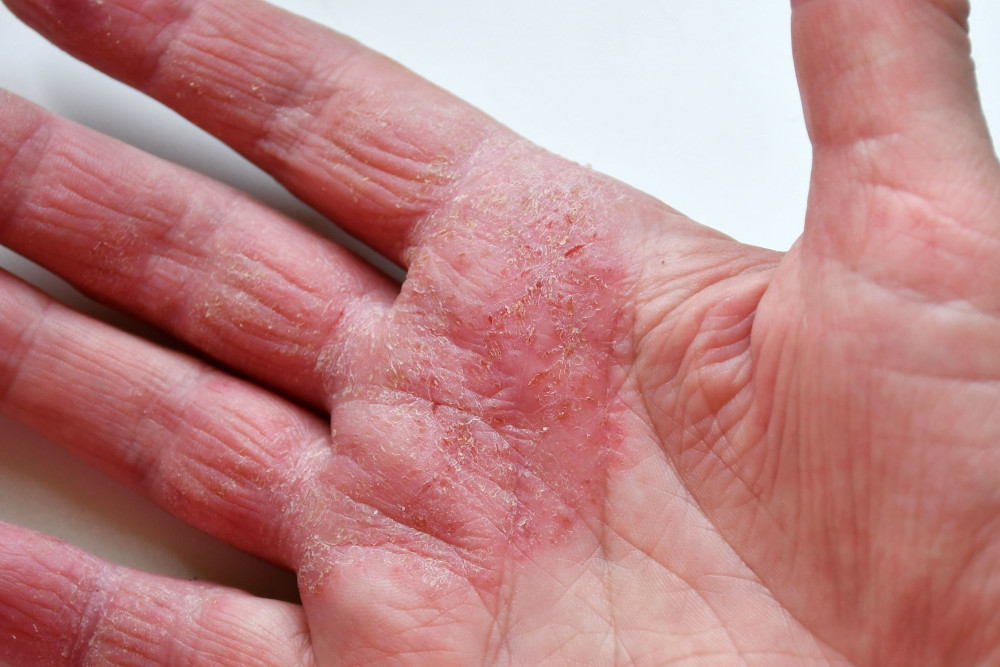
Dermatitis and Eczema
What is Dermatitis and Eczema?
Dermatitis is a group of inflammatory skin conditions that cause itchiness, redness, and changes in the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). It disrupts the skin’s barrier, leading to symptoms like flaking, swelling, and rashes. While often used interchangeably with eczema, dermatitis is a broader term encompassing all types of skin inflammation, whereas eczema specifically involves swelling in the top layer of the skin called epidermis.
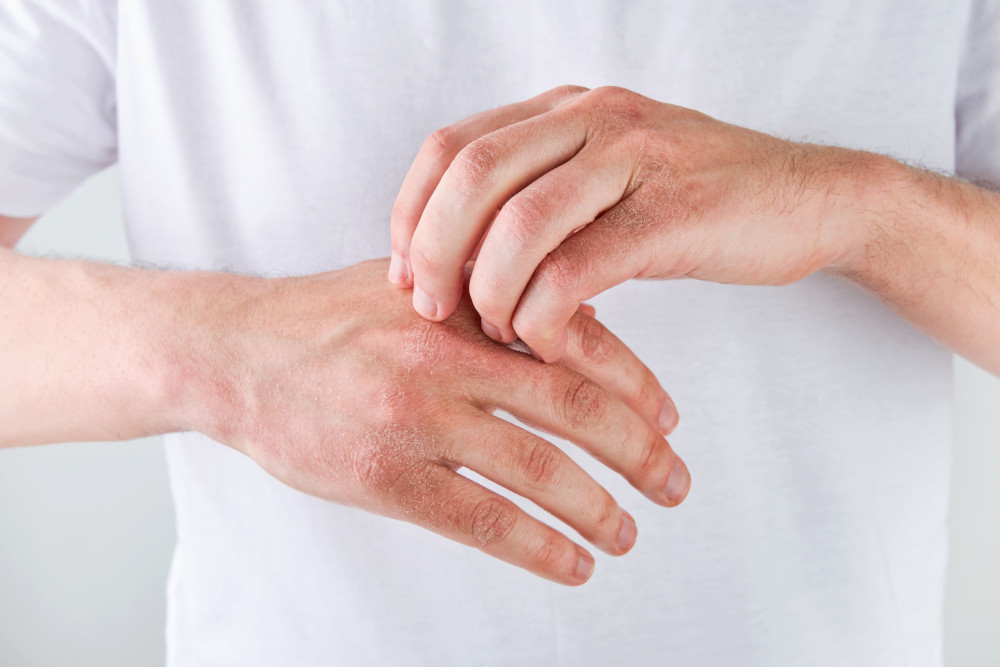
Common Symptoms of Dermatitis
- Redness, heat, and flaking skin
- Swelling in the skin and itchy rashes
- Rough, dry patches or weeping sores
- Symptoms can range from mild irritation to severe body wide rashes
Dermatitis can affect any part of the body, including the face, scalp, hands, and legs. Severity and symptoms vary between individuals, with some experiencing occasional dryness and others suffering frequent flare-ups.
Who is Affected by Dermatitis?
Dermatitis is a common condition that affects 1 in 5 people at some stage in life. It occurs across all age groups:
- Children: Atopic dermatitis and pityriasis alba are more common.
- Young and middle-aged adults: Hand eczema is frequent.
- Older adults: Conditions like venous eczema and asteatotic dermatitis are prevalent.
While dermatitis is not limited by race or gender, individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies may have a higher risk. Stress and environmental factors can also trigger symptoms.
Types of Dermatitis
Dermatitis is categorized into exogenous (caused by external factors) or endogenous (due to internal causes).
Endogenous dermatitis occurs due to internal factors that are often not fully understood. There are various subtypes of this condition.
The exogenous dermatitis can be classified depending on the causative factor, and the main subtypes are –
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by allergens like nickel, perfumes, or rubber.
- Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Caused by exposure to irritants (e.g., soaps, detergents, solvents).
- Photosensitive Dermatitis: Induced by light or UV exposure.
- Post-Traumatic Dermatitis: Triggered by physical injuries like burns or abrasions.
- Infectious Dermatitis: Due to bacterial, fungal, or viral skin infections.
- Drug-Induced Dermatitis: Caused by certain medications.
What Worsens Dermatitis?
Dermatitis often results from an impaired skin barrier. This leads to inflammation and itching caused by a release of histamine in response to irritation or allergens. Scratching the skin worsens the cycle, triggering the body to release more histamine and intensifying the symptoms.
Stress, genetics, environmental triggers, and exposure to irritants can worsen dermatitis. Flare-ups may also occur without any identifiable trigger.
How is Dermatitis Treated?
While dermatitis cannot always be cured, effective treatment can manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Avoiding Triggers
- Identify and avoid allergens and irritants.
- Use protective gloves to shield hands during work or cleaning.
- Switch to fragrance-free and gentle skin products.
Topical Therapies
- Emollients: Moisturize the skin and replace soaps.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal alternatives for sensitive areas like the face.
Physical Therapies
- UVB Phototherapy: A safe, controlled treatment for severe or resistant cases. Narrowband UVB (nbUVB) phototherapy is a safe, effective eczema treatment that has provided excellent results and significant relief of eczema symptoms for many years.
Systemic Treatments
- Antihistamines: Relieve itching.
- Antibiotics/Antivirals: Treat secondary bacterial or viral infections.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like methotrexate and cyclosporine for severe conditions.
- Biological Therapies: Advanced options targeting specific inflammatory pathways
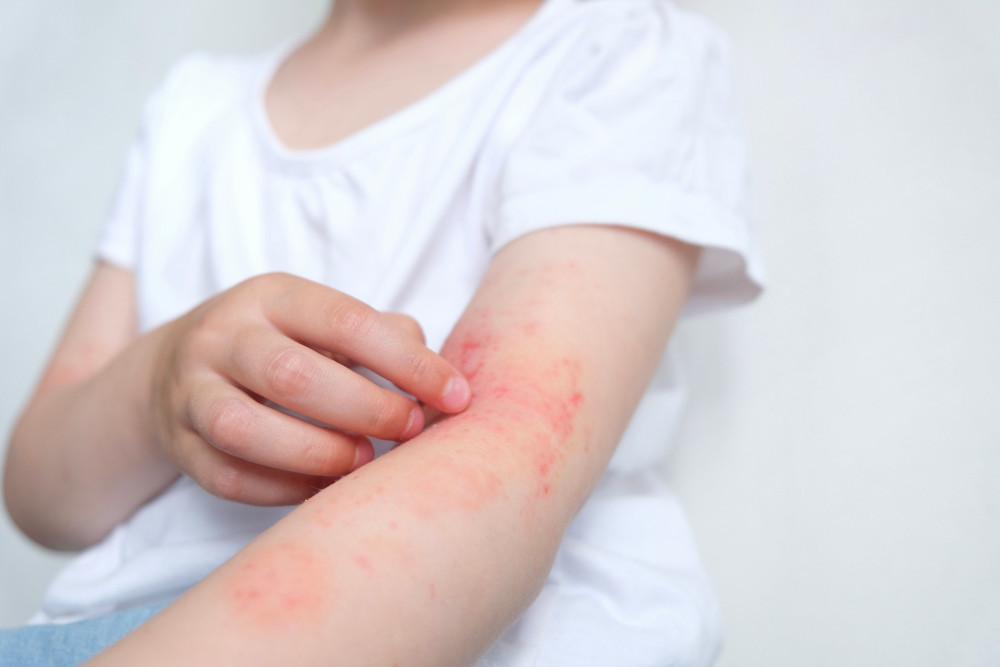
Managing Dermatitis Symptoms
Dermatitis can severely impact daily life, leading to discomfort, disturbed sleep, and even anxiety or depression. Visible symptoms on areas like the face or hands can affect self-confidence and relationships. Proper management involves:
- A tailored treatment plan
- Education on how to protect and repair the skin barrier
- Regular follow-ups and adjustments to treatment
We are committed to empowering you with the knowledge, tools, and treatment options needed to reduce the discomfort of eczema and maintain your skin’s health for the long term. No matter your age, profession, or personal circumstances, managing eczema is essential for improving your overall health and quality of life. Book your initial consultation and take the first step toward managing your dermatitis effectively.
Other Skin Disorders:
Eczema Links and FAQs
- What is Eczema? https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema/
- Eczema Home Care Programme https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/home-care-programme/
- Skin Products for Eczema to buy online https://www.theskinnetwork.com.au/collections/eczema?page=2
- Topical Skin Creams for Eczema https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/topical-therapy/
- UVB Phototherapy for Eczema https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/uvb-phototherapy/
- Systemic Therapy for Eczema https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/systemic-therapy/
- Eczema Clinics Australia https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/about-us/
- Eczema Support Groups Australia https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/eczema-support-groups-in-australia/
- Diet and Lifestyle Modification for Eczema https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/living-with-eczema-diet-and-lifestyle-tips/
- Eczema in Babies https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/best-products-for-baby-eczema/
- Eczema and Sensitive Skin https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/eczema-and-sensitive-skin-in-australia/
- Best Natural Treatments for Eczema https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/best-natural-treatments-for-eczema/
- Top Eczema Triggers to Avoid https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/top-eczema-triggers-to-avoid/
- Managing Eczema Flare ups https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/eczema-support-guides-and-updates/managing-eczema-flareups/
- Eczema and Stress https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/can-eczema-be-caused-by-stress-2/
- Can Eczema be Cured? https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/can-eczema-be-cured-2/
- Eczema Clinics Australia https://eczemaclinicsaustralia.com.au/contact/